Whether you are looking to build a new home or buying a resale property, paying close attention to the insulation in your home is important when it comes to your comfort and cost savings. Home builders in Edmonton and St.Albert can easily combine the right amount of insulation and ensure the correct placement so that your home can become more energy efficient. Effective insulation will slow down the transfer of heat and prevents air from flowing easily between larger openings as well as gaps in the home.
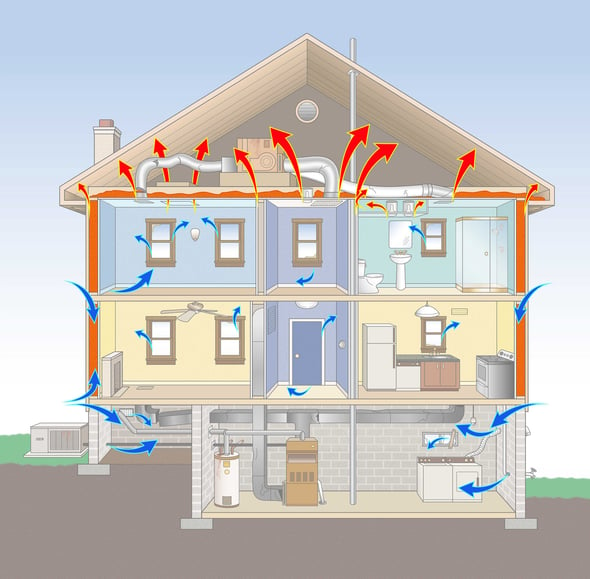
Heat loss happens for a few reasons. Conduction through ceilings, walls and floors moves heat through the transfer of thermal energy. We lose significant heat through the wood frames, steel beams and concrete and these materials are known as thermal bridges. Heat moves through the convection of air motion due to warmer air rising and cooler air falling. Air loss is affected when there are significant temperature differences inside and outside of your home. Radiation from the sun also moves energy into a home by changing the temperature coming from your attic.
Understanding R-value
Insulation is rated using an R-value, which is a measure of a material’s resistance to heat flow. The higher the R-value, the more resistant a material is to heat loss and heat gain. The density and thickness of the insulation will measure how effectively the insulation limits the movement of energy. Insulation can be distinguished by its specific R-value and not all types of insulation will be the same. If the R-value of your wall doubles, the amount of energy you’re losing is cut in half. Thermal bridges affect the overall R-value of a wall system is usually less than that of the R-value of the insulation itself. However, doubling your insulation amounts does not necessarily mean that you are doubling your overall R-value.
Manufacturers are required to disclose the R-Value rating of their products and obtaining the information is relatively easy by checking with the product type or by looking at the builder’s specifications. It is important to know the different types, location and the R-value of the insulation being used and compare them to the industry standards used today.
Insulation Types
Because not all insulation will give you the same R-value, here are the 4 most common types of insulation used in homes:
- Batt Insulation

Batt insulation is one of the most conventional forms of insulation used today. It is known to be effective against conductive heat loss. Batts are made up of pre-cut fiberglass or rock wool sections that are designed for simple handling. The most common places you will find batt insulation is between framing, such as studs and joists. Batt insulation may not completely cover all areas of your home however it is used together with exterior air barriers like Tyvek and interior vapor retarders like polyethylene.
- Blown-In or Loose Fill

Blown-in or loose fill insulation typically consists of fiberglass or cellulose (recycled paper fibre). The insulation is sprayed or blown into place by machine and is truly convenient for hard-to-reach areas, such as attics. It can also be used to top off existing insulation or to fill wall cavities. Compared to batt insulation, the loose fill will have a higher density and be more stable in adverse weather conditions.
- Foam Board

Foam board insulation is generally made up of polystyrene and polyurethane, and can be used to insulate almost any part of your home. It can sometimes be referred to as ‘Sheet Insulation’ or ‘Rigid Insulation’. From the roof to the foundation, foam board is typically easy to install and comes in a variety of thicknesses. The sheathing reduces heat conduction through structural elements like wood and steel studs. A layer of insulating foam on the outside of exterior walls also helps the framing stay dry by raising the dew point of the surface where water vapor is likely to condense.
- Spray Foam

Spray Foam, made up of latex or polyurethane can be used to fill small gaps and is ideal for sealing around doors, windows and vents. It has a few different properties such as the ability to set quickly, be trimmed, painted or stained. Special equipment may be needed to apply foam to larger areas. Because spray foam insulation is self-supporting, it will work well in closed wall cavities and unsupported areas. Spray Foam Insulation is easily installed in hard-to-reach spots and is resilient over the years. At Kanvi Homes we spray foam our rim joists to help seal the home from the elements.
Have you ever wanted to see our custom homes at a framing stage? It could be a great way to view the types of insulation we use. Contact us to see the Kanvi difference or visit our show homes.